Whether you're a budding amateur mechanic or prefer to never touch a wrench, knowing how your
Mustang's engine works is essential. This can be helpful if you are considering
aftermarket engine upgrades or are trying to better understand a repair estimate. In
this article, we'll look at Mustang camshafts vs
crankshafts.
While these are two separate engine components that each serve a unique function, a camshaft
and crankshaft must operate together for the proper performance of your Mustang engine.
Engine Types
Camshafts
Crankshafts
Camshafts vs Crankshafts
Timing Chain/Belt
Upgrade
Depending on the age of your Mustang, the car's powerplant will have either a "pushrod"
overhead valve (OHV) or overhead cam engine (OHC) configuration. While engine setup will
determine camshaft location, the overall functions of and interdependence between the
camshaft and crankshaft will remain the same regardless if your car has an OHC or OHV
engine. Be sure to check out a related Steeda article, Mustang Pushrod vs Overhead Cams,
for more engine information. A single cam in an overhead valve engine is located between the engine's cylinders. Using a
set of pushrods, the camshaft engages the intake and exhaust valves. This is why OHV
engines are called pushrods. Pushrod engines were popular in the Mustang until the 1990s
and continue to be popular in some General Motors models. Depending on the OHC engine configuration, a single camshaft or multiple cams be used with
each bank of cylinders. The camshafts are located on the top of the cylinder heads and
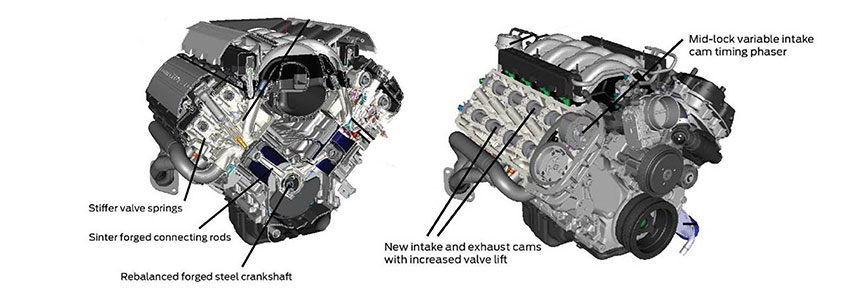
engage the intake and exhaust valves during rotation. You may ask, "what is a camshaft?" A camshaft, or cam for short, is a metal rod intersected
with various sized metal lobes that may look like a teardrop or similar shape. When the
lobes rotate, they engage the intake and exhaust valves with rocker arms in an overhead
cam engine or through pushrods in an overhead valve engine. Modern Mustang engines rely on a multiple camshaft configuration to help improve performance
and fuel efficiency--this is the appeal of OHC engines as automakers can highlight more
powerful cars while meeting or exceeding government fuel economy mandates. This
"quad-cam" design happens through a single camshaft controlling the intake and exhaust
valves on each bank of engine cylinders. Known as variable camshaft timing (VCT) or Twin
Independent Variable Camshaft Timing (Ti-VCT) in Ford speak, this technology allows the
camshafts to change the speed of the intake and exhaust valves as needed. Keep in mind that camshaft "lift" is generally a good thing, to a point. More lift allows for
greater airflow through the valves, which usually means improved engine performance.
However, excessive lift causes "valve float," which can cause the engine to over-rev and
lose performance. Ideal lift permits the optimal amount of air as the valve travels in
sync with the camshaft. Also, there are multiple aftermarket crankshaft options that
enable turners to modify lift and improve engine performance. Next, let's answer the "what is a crankshaft?" question. At the base of your Mustang's
engine, underneath the cylinders, is the crankshaft that moves the engine pistons. The
pistons are joined to the crankshaft by the connecting rods, so the pistons move up and
down as the crankshaft rotates. As the pistons move up, the mixture of air and fuel is
compressed and ignited in the cylinder. This creates a reciprocating motion that then
forces the pistons down to draw in more air and fuel. This is the four-stroke cycle that defines the essential operations of most internal
combustion engines. For a crankshaft to properly operate—as well as the engine
itself—the camshaft controlled intake and exhaust valves must function perfectly as
well. The precise operation of the intake and exhaust valves along with the pistons, camshafts, and
crankshaft is all about timing. This is accomplished through a timing belt or timing
chain that connects the camshafts and the crankshaft. Don't think of this as camshafts
vs. crankshafts, but rather how all these vital components work together. Comprised of a rubber composite, timing belts are more cost-effective for the manufacturer
than a timing chain. Also, these belts tend to produce less engine noise than a timing
chain. Similar to what you'd find on a bicycle, timing chains are a roller-style chain
that offers more durability than a timing belt but requires continuous lubrication. First-generation Mustangs used timing chains. However, some Mustang II and Fox Body models
were equipped with timing belts as a cost-saving move by Ford. Starting with the
mid-1990s and the SN95 generation launch, Ford switched all Mustangs to a timing chain
configuration to improve durability, especially as the more complex OHC engines (Ford's
modular V-8s) replaced the pushrod powerplants. Check the factory maintenance schedule or contact a Ford dealer to determine your Mustang's
timing configuration and service requirements. A malfunctioning timing chain or timing belt should be looked at right away. A chain or belt
failure can cause a piston to strike a valve resulting in significant and expensive
engine damage. Pay attention to frequent backfiring, rough engine idle, or a
high-revving engine that produces minimal movement. These are all signs that the timing
between the camshafts and crankshaft is no longer synced. Get this checked out
immediately. While not as showy as some aftermarket body parts or rims, a performance-enhancing camshaft
can help deliver a power upgrade to your Mustang. Aftermarket camshafts incorporate
different-shaped lobes that are designed to create a higher lift. As we mentioned
earlier, it's all about finding the perfect formula for increasing air and exhaust flow
without overwhelming the engine. There are several important factors when considering a camshaft upgrade: Always consult with an aftermarket expert or experienced service technician before moving
forward with a camshaft replacement project.Mustang Camshafts vs Crankshafts Explained


Mustang Engine Types

Mustang Camshafts Explained

Mustang Crankshafts Explained
Mustang Camshafts vs Crankshafts

When To Replace The Timing Chain Or Timing Belt

Upgrade Your Mustang Camshaft(s)
Related Articles




